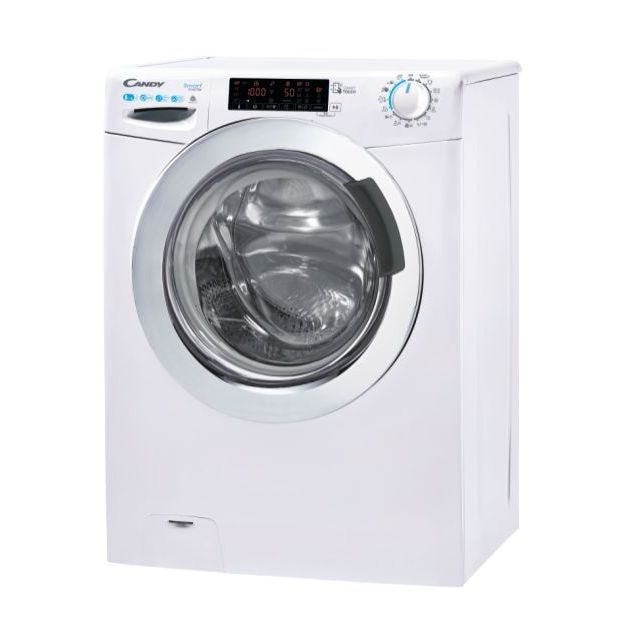
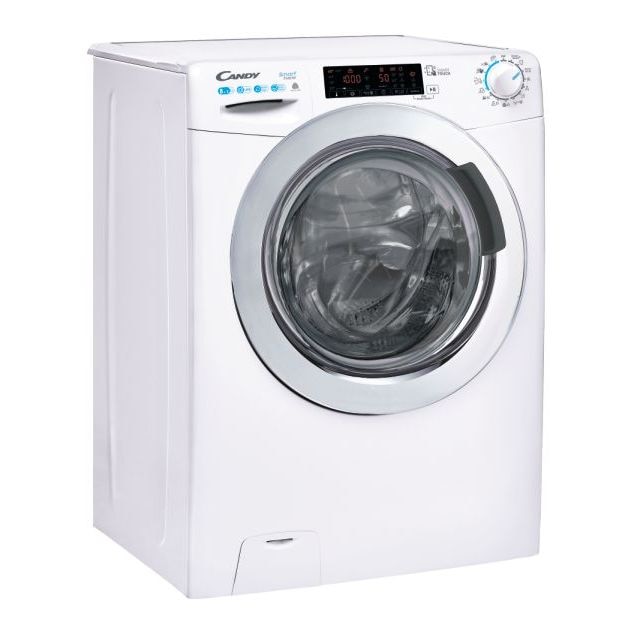
Candy CSWS485TWMCE/1-S mosó-szárítógép, 8kg, 5kg szárítókapacitás, 16 program, A/D energiaosztály, 1400 fordulat/perc, Fehér - eMAG.hu

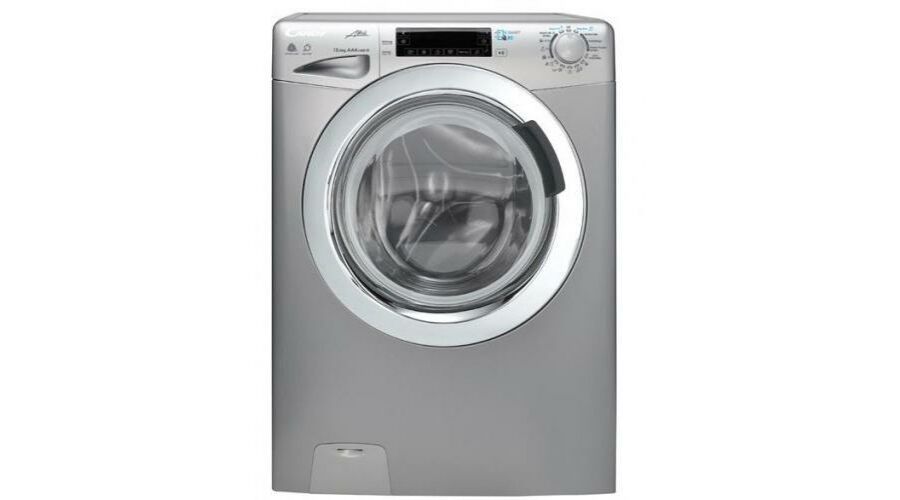
Candy CBDO485TWME-S Beépíthető mosó-szárítógép, 8kg mosó kapacitás, 5kg szárító kapacitás, 1400 fordulat/perc, 16 program, A energiaosztály, Fehér - eMAG.hu