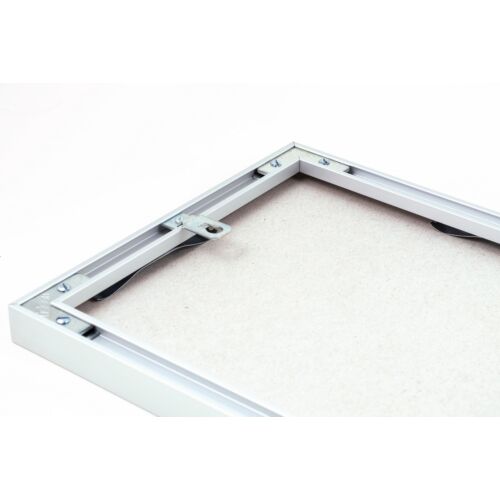
Fém képkeret 70 x 100 cm - Matt ezüst - Fém képkeretek - Képkeretezés és poszter Budapesten | Darvas Képkeret
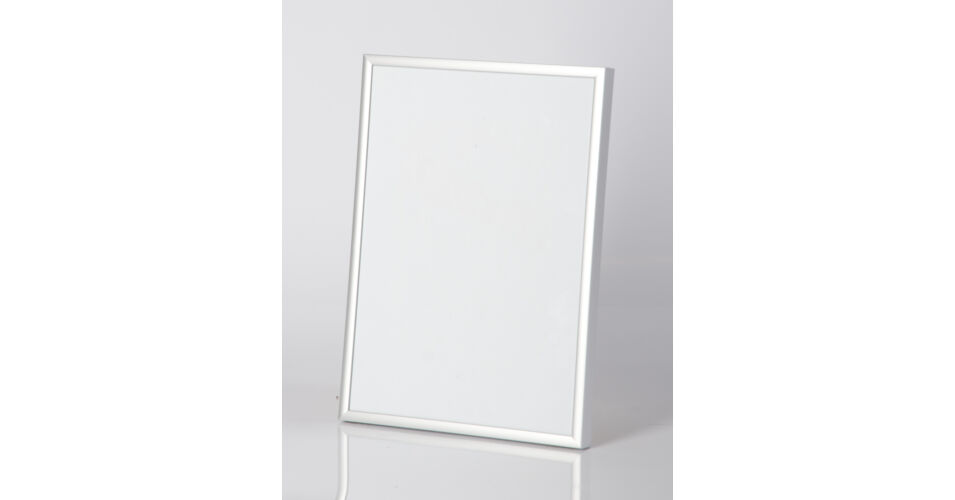

Fém képkeret 70 x 100 cm - Matt ezüst - Fém képkeretek - Képkeretezés és poszter Budapesten | Darvas Képkeret
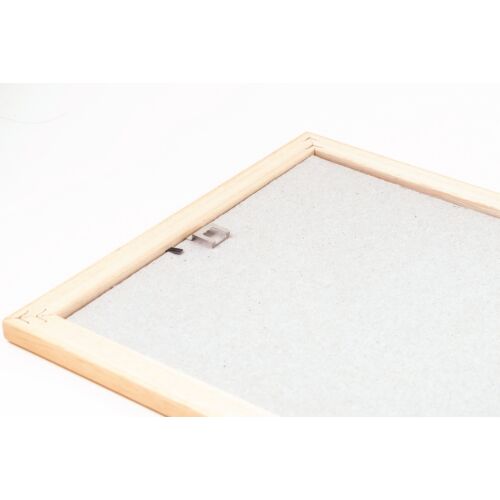

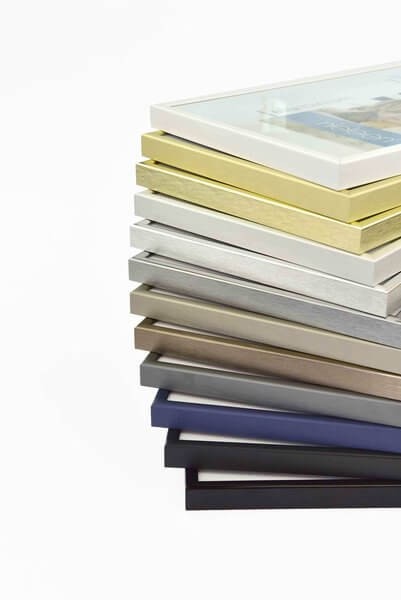
Fa képkeret 50 x 70 cm - Fehér - Vastag keretek - Képkeretezés és poszter Budapesten | Darvas Képkeret
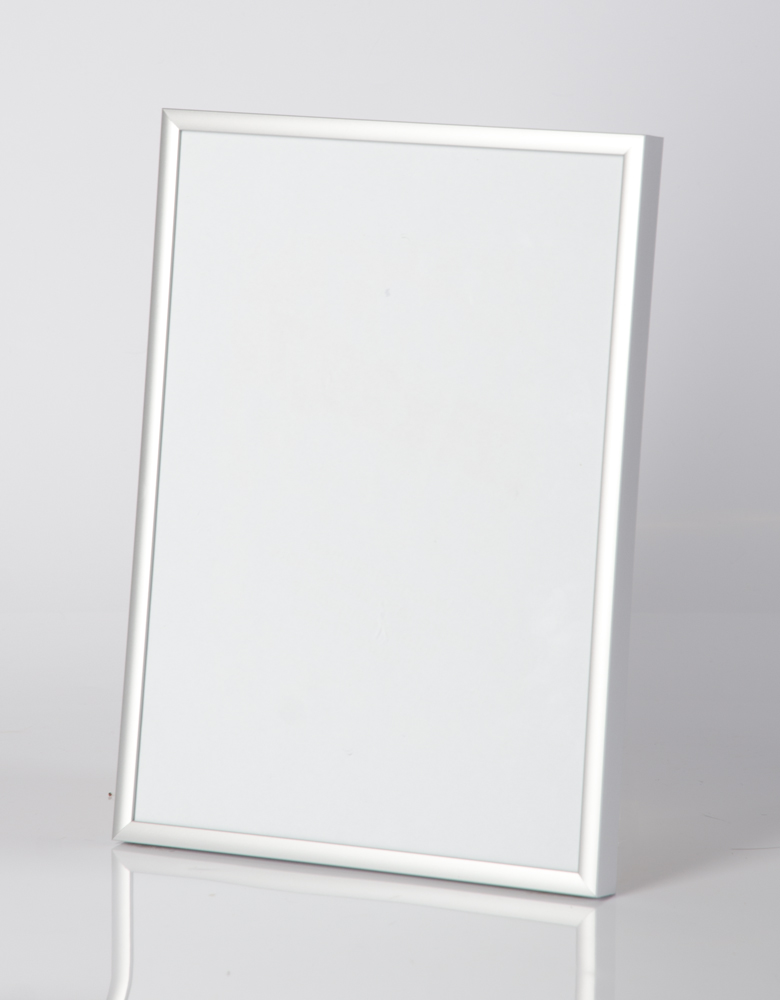

Fém képkeret 70 x 100 cm - Matt ezüst - Fém képkeretek - Képkeretezés és poszter Budapesten | Darvas Képkeret
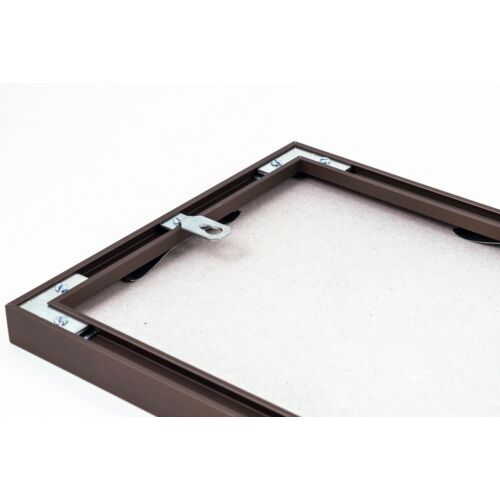

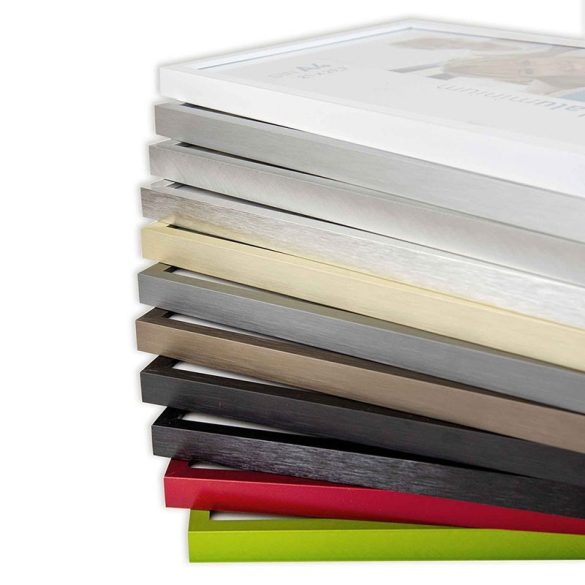
Fém képkeret 70 x 100 cm - Matt bronz - Fém képkeretek - Képkeretezés és poszter Budapesten | Darvas Képkeret

Fém képkeret 70 x 100 cm - Matt bronz - Fém képkeretek - Képkeretezés és poszter Budapesten | Darvas Képkeret

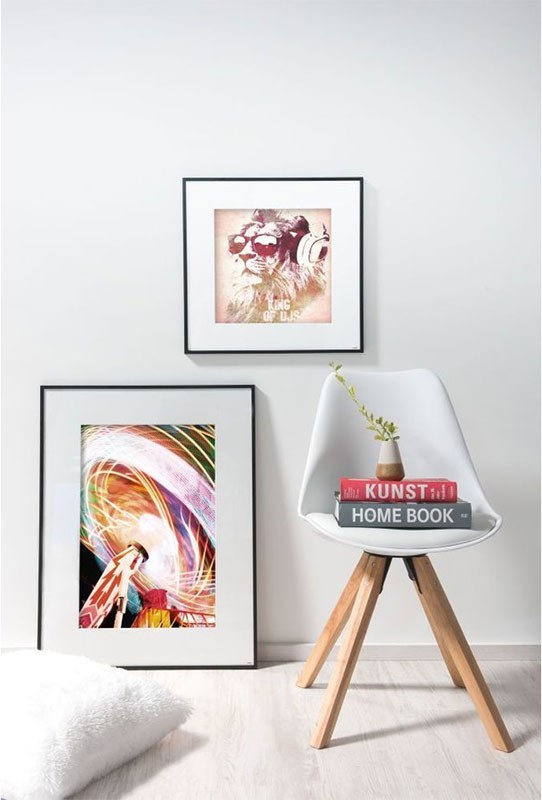
Hosszúkás - cirádás fali képkeret - 70x20 cm - fehér - Dísz fényképkeret - Fényképkeretek - Több képes - Ajándék - Ajándék, játék, jelmez és iskolafelszerelési áruház, webáruház.